The nature of defect tolerance in (some) halide perovskites
The halogen vacancy, Tl-activator, and Tl-bound excitons in CsI:Tl scintillator
Presentation on Cs2HfCl6
Case of the Bromine Vacancy in Cs4PbBr6 (Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters)
Revisiting the origin of green emission in Cs4PbBr6 (Materials Advances)
Metal Halide Semiconductors beyond Lead-Based Perovskites for Promising Optoelectronic Applications (Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters)
Phase transition pathway of hybrid halide perovskites under compression: Insights from first-principles calculations (Phys. Rev. Materials)
New Polymorphs of 2D Indium Selenide with Enhanced Electronic Properties (Advanced Functional Materials)
Book Chapter: Perovskites – Revisiting the Venerable ABX3 Family with Organic Flexibility and New Applications, in Optical Properties of Materials and Their Applications, 2nd Ed. (Wiley)
Impact of organic molecule rotation on the optoelectronic properties of hybrid halide perovskites (Physical Review Materials)
Sept. 2019 – Condensed Matter Seminar, Texas A&M University, Hybrid and All-Inorganic Perovskites
Computational Design of Mixed-Valence Tin Sulfides as Solar Absorbers (ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces)
Nov. 2018 – Perovskite-type Halides as Highly Luminescent Materials, 2018 IEEE Nuclear Science Symposium, Sydney
Oct. 2018 – Seminar, University of Memphis, Structural and Property Trends Among Complex Halides
June 2018 – Seminar, Jilin University, A Brief Perspective on Halides as Optoelectronic Materials
Exploring Polaronic, Excitonic Structures and Luminescence in Cs4PbBr6/CsPbBr3 (Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters)
Bismuth and antimony-based oxyhalides and chalcohalides as potential optoelectronic materials (npj Computational Materials)
InSe: a two-dimensional material with strong interlayer coupling (Nanoscale)
Comparative study of perovskite-type scintillator materials CsCaI3 and KCaI3 via first-principles calculations (J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys.)
Shallow trapping vs. deep polarons in a hybrid lead halide perovskite, CH3NH3PbI3 (Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys.) Inside Cover

Preferential CH3NH3+ Alignment and Octahedral Tilting Affect Charge Localization in Cubic Phase CH3NH3PbI3 (Journal of Physical Chemistry C)
Emerging New Pseudobinary and Ternary Halides as Scintillators for Radiation Detection (IEEE Transactions on Nucl. Sci.)
The role of hydroxyl groups in interchain interactions in cellulose Iα and Iβ (Int. J. Quantum Chemistry) Cover Image
Jonathan presented at 2017 NCUR (Memphis)

Ramifications of codoping SrI2:Eu with isovalent and aliovalent impurities (J. Appl. Phys.)
A first-principles based study of ns2 containing ternary iodides and their possibility of scintillation (J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys.)
Carrier Self-trapping and Luminescence in Intrinsically Activated Scintillator: Cesium Hafnium Chloride (Cs2HfCl6) (Journal of Physical Chemistry C)
Quaternary Iodides A(BaSr)I5:Eu2+ (A = K, Cs) as Scintillators for Radiation Detection (Journal of Physical Chemistry C)
Preferential Eu Site Occupation and Its Consequences in the Ternary Luminescent Halides AB2I5∶Eu2+ (A=Li–Cs; B=Sr, Ba) (Physical Review Applied)
A short video!
Jay Mayfield presents at the 8th Annual ARI Grantees Meeting (U T Dallas; July 7-9, 2015) Student Presentation
DX-like centers in NaI:Tl upon aliovalent codoping (J. Appl. Phys.)
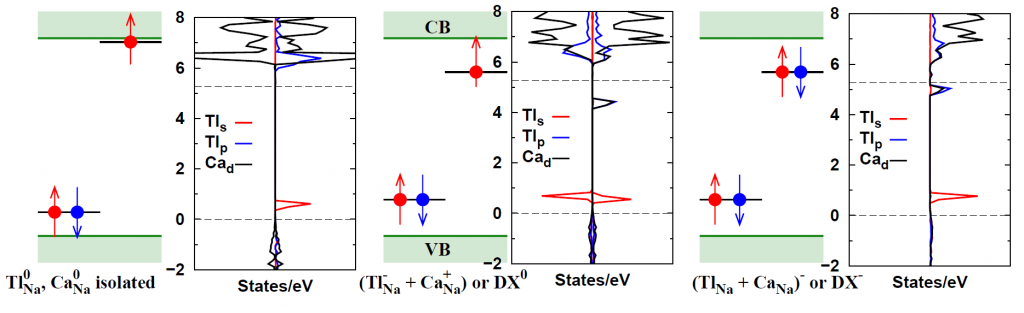
Aliovalent doping has been recently shown to remarkably improve energy resolution in some halide scintillators. Based on first-principles calculations we report on the formation of DX-like centers in a well-known scintillator material, Tl-doped NaI (NaI:Tl), when codoped with Ca or Ba. Our calculations indicate a net binding energy favoring formation of the defect complex (Tl_Na+Ca_Na) involving a new cation-cation bond, instead of the isolated substitutional defects. The pair has properties of a deep DX-like acceptor complex.


